Do you ever wonder how the way you sit during the workday impacts your well-being? Ergonomics play a major role in your health, comfort, and productivity.
Poor posture, incorrectly positioning your screen, and sitting in the wrong kind of chair are some of the most common mistakes that deskworkers make. Over time, these errors can lead to pain, fatigue, and reduced focus.
Understanding and correcting these typical office ergonomics mistakes is crucial to feeling and working well throughout the day.

What Is an “Ergonomic Problem”?
Ergonomic problems are complications that arise when your workspace isn’t made to fit your physical and cognitive needs. When you make your workspace more ergonomic, you optimize your comfort and efficiency and minimize your risk of injury and musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs).
Why Does Ergonomics Matter?
Poor ergonomics majorly impacts your health and well-being. Sitting with incorrect posture for long hours can not only cause back, shoulder, neck, and/or wrist pain but also lead to chronic conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
Beyond the physical consequences, improper office ergonomics can reduce your focus and productivity, cause fatigue, and lead you to make more mistakes in your work. Making sure that your workspace is ergonomic—whether in the office or, in the case of remote work, at home—is essential to feeling and working your best!
Common Ergonomics Mistakes

Poor Posture
Sitting with poor posture—for example, slouching or sitting too stiffly—is a major cause of ergonomic problems. It frequently leads to pain and tension in the lower back in particular.
Approximately 20-60% of office workers worldwide suffer from musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), and 30% of sick days in the United States have MSDs at their root.
These statistics prove exactly how important it is to prioritize a healthy posture and invest in ergonomic solutions.
Solutions:
- Use an ergonomic chair
- Adopt a good posture
- Alternate between standing and sitting to reduce tension
Improper Desk Height and Screen Height
A screen that’s too high or too low can cause neck pain and tension. Discomfort in the neck and shoulders can also put you in a bad mood, making the workday feel longer and harder to get through.
A San Francisco State University study found that the head-tilting caused by a badly-positioned screen can make your neck and head almost four times heavier on your upper back. The pain and stiffness this extra weight causes negatively impacts your productivity and well-being. Adjust the height and angle of your screen to promote a healthier, more comfortable posture.
Solutions:
- Place the screen at eye-level, 20 to 30 inches from your face
- Adjust the height of your desk so that your elbows are positioned at a 90° angle to it. Follow our advice for an ergonomic workspace.
Incorrect Seat
A non-ergonomic or badly-adjusted chair is a common cause of back pain, especially in the lower back. A lack of appropriate support can lead to tension in the spine, provoking acute or chronic pain.
Moreover, a seat that’s positioned too high can prevent your feet from touching the ground, while a seat that’s too low puts an excessive bend in your knees, disrupting your circulation.
In the long term, poor posture can aggravate ergonomic problems and diminish your comfort and productivity.
Solutions:
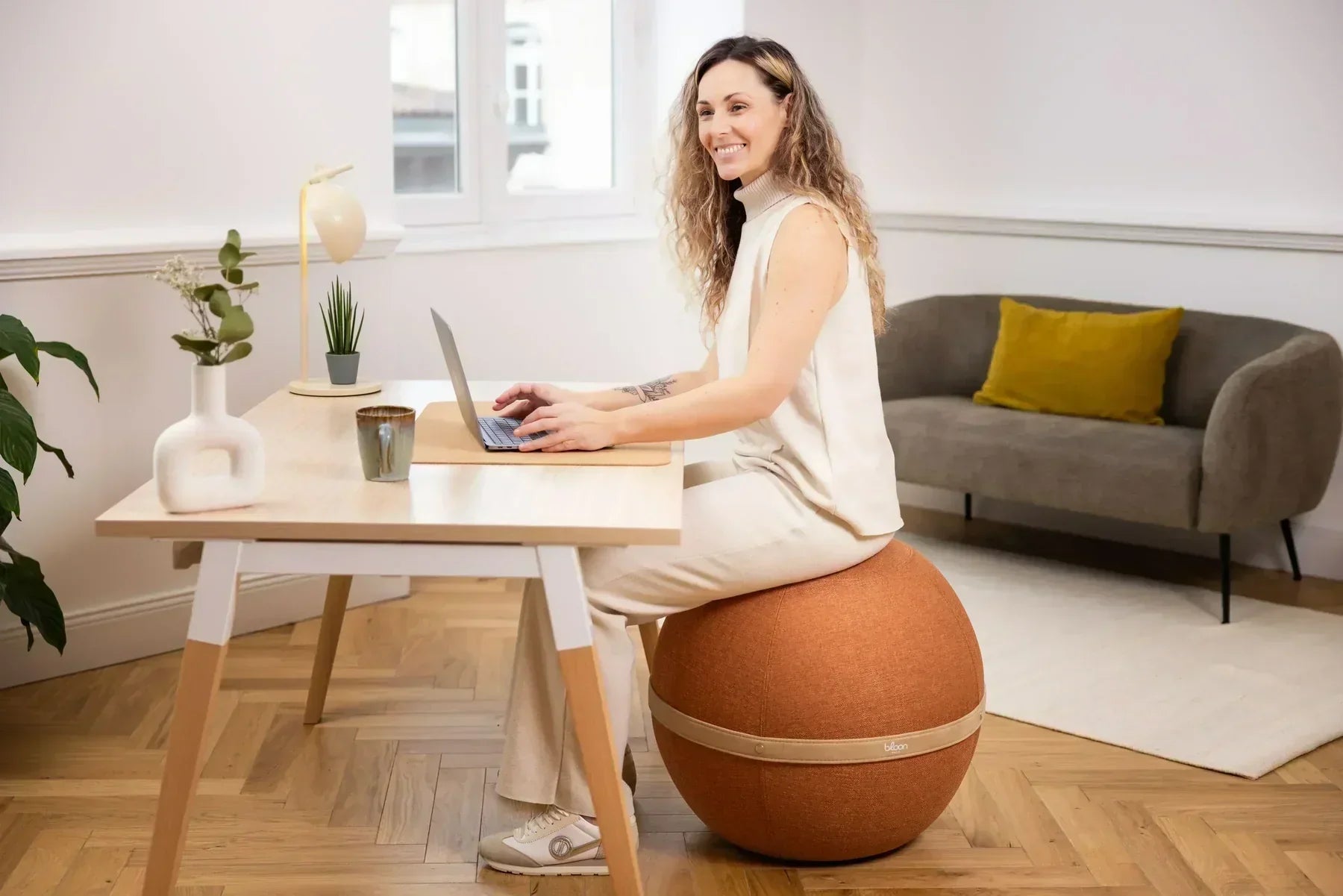
- Use an ergonomic chair like the Bloon ball seat
- Adjust your chair’s height so that it’s correctly aligned with your desk
Improper Arm and Wrist Position
The way you position your arms and wrists while typing can have serious health consequences.
According to the United States Bone and Joint Initiative, over half of all adults in the U.S. suffer from musculoskeletal disorders. Working at a desk increases the risk of certain conditions. In one study, over one-third of the people studied that had carpal tunnel syndrome worked desk jobs like management, finance, and administration.
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the wrist’s medial nerve is compressed. It can lead to pain, numbness, and even weakness in the hands.
These problems are often aggravated by the prolonged use of a keyboard or mouse without adequate support in the arms and wrists.
Solutions:
- Position your keyboard at the correct height, with your wrists straight
- Maintain a natural posture in the arms and wrists
- Use an ergonomic mouse and keyboard.
Sitting Still for Too Long
Sitting in the same position for too long makes you more likely to experience musculoskeletal troubles and muscular stiffness. These ergonomic problems are particularly common in people who work from home. Remaining in one position places greater stress on the muscles and joints, since they have to hold your weight in the same place for longer. That stress can lead to chronic pain.
Solutions:
- Take breaks every hour
- Use a standing desk to change your posture
- Do some light stretching to release muscle tensions.

Inadequate Lighting
According to recent studies, around 65% of Americans suffer from Digital Eye Strain, a condition generally linked to inadequate lighting and/or to long hours looking at screens.
Bad lighting can cause headaches, blurry vision, or eye pain—tacking more complications onto other workplace ergonomics problems. These symptoms don’t just impact your visual comfort but also your productivity and focus.
Solutions:
- Use soft, natural lighting as often as possible
- Install adjustable lamps to prevent glare
- Reduce blue light exposure with a filter
FAQ: Everything You Need to Know About Office Ergonomics
What is an Ergonomic Problem ?
An ergonomic problem occurs when your work environment, tools, and posture create discomfort or health risks. These problems can in turn lead to pain, fatigue, or reduced productivity.
What are the 7 Ergonomic Risk Factors?
The 7 primary ergonomic risk factors are:
- Uncomfortable posture or prolonged sitting
- Repetitive movement
- Applying excessive force
- Vibrations
- Localized pressure
- Extreme temperatures
- Inadequate lighting
What Are Ergonomic Constraints?
Ergonomic constraints are physical (posture, repetitive movement), organizational (schedule, work rhythm), and environmental (lighting, noise, temperature) factors that can impact ergonomics.
What Are the 3 Types of Ergonomics?
The 3 types of ergonomics are:
- Physical ergonomics: Focuses on the human body and its biomechanics
- Cognitive ergonomics: Focuses on mental processes, like focus and decision-making
- Organizational ergonomics: Focuses on work systems and methods
What Is Workplace Ergonomics?
Workplace ergonomics involves adapting the workspace, tools, and environment to the abilities and needs of the employee in order to prevent injuries and maximize performance.
What are the Three Pillars of Ergonomics?
The three pillars of ergonomics are: physical ergonomics, cognitive ergonomics, and organizational ergonomics.
How Do I Improve the Ergonomics of My Office?
Practical ways to improve the ergonomics of your office include:
- Sitting with correct posture and adequate back support
- Making sure your screen is correctly positioned to prevent neck pain
- Using an ergonomic and adjustable chair
- Taking regular breaks to move and rest your eyes
What Ergonomic Factors Can Negatively Impact My Well-Being?
Bad lighting, sitting still for too long, inappropriate work tools, and unhealthy work rhythms can all negatively impact your well-being.
How Do I Make My Desk More Ergonomic?
- Adjust your desk and seat to promote a more natural posture
- Adjust lighting to reduce glare
- Use tools like ergonomic keyboards and mice
What Defines Proper Ergonomics?
Proper ergonomics integrates comfort, safety, and effectiveness to prevent injuries and improve your quality of life at work.
What Risks Does Office Ergonomics Aim to Reduce?
Office ergonomics aims to reduce the risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) as well as the physical and mental fatigue linked to poor workplace conditions.
What Are Some Constraints to Ergonomics?
Constraints can include the cost of ergonomic equipment, a person’s resistance to changing their habits, and a lack of awareness on the part of employees and employers.
What Ergonomic Tools Exist?
Some common ergonomic tools are ergonomic seats, sitting-standing desks, standing mats, screen stands, and ergonomic keyboards and mice.
Why Is Office Ergonomics Important?
Office ergonomics is important because it prevents pain, improves employee well-being, and improves poductivity and satisfaction at work.
By correcting your ergonomic mistakes with these helpful hints and tips, you can considerably reduce your risk ergonomic problems, whether you’re working from home or in the office.